司巴丁
 | |
| 臨床資料 | |
|---|---|
| 其他名稱 | (左旋)金雀花鹼、司巴汀、鷹爪豆鹼、無葉豆鹼、Tocosamine |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | 國際藥品名稱 |
| ATC碼 | |
| 識別資訊 | |
| |
| CAS號 | 90-39-1 |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.808 |
| 化學資訊 | |
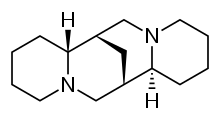
| 化學式 | C15H26N2 |
| 摩爾質量 | 234.39 g·mol−1 |
| 3D模型(JSmol) | |
| 密度 | 1.02 g/cm3 |
| 熔點 | 30 °C(86 °F) |
| 沸點 | 325 °C(617 °F) |
| 水溶性 | 3.04 mg/mL (20 °C) |
| |
| |
司巴丁(INN:sparteine),又稱(左旋)金雀花鹼、鷹爪豆鹼等[1]。是存在於金雀花、南美羽扇豆、鷹爪豆等豆科植物中的生物鹼[2],是一種Ia類抗心律失常藥和鈉離子通道阻滯劑。同時也是一種螯合劑,能與Ca2+,Mg2+等二價金屬離子螯合。司巴丁沒有通過FDA批准用於抗心律失常藥物,同時也沒有在抗心律失常藥物辛格-威廉姆斯分類名單中。
在有機化學中,司巴丁常作為手性配體,特別是涉及有機鋰試劑,會常用到司巴丁。
生物合成
[編輯]
司巴丁是一種羽扇豆生物鹼,其分子包含由三個L-賴氨酸分子衍生出來的四環雙八氫喹嗪結構[3]。在其生物合成過程中,首先由賴氨酸經過賴氨酸脫羧酶(LDC)合成1,5-戊二胺中間體[4]。三個1,5-戊二胺隨後組成八氫喹嗪骨架。目前已經通過酶促和放射性元素示蹤研究了司巴丁形成機制,但確切的合成途徑仍不清楚。
研究者採用了13C-15N雙標記的1,5-戊二胺來研究合成過程,結果顯示1,5-戊二胺單元整合到到司巴丁分子中,並且兩個1,5-戊二胺分子中的兩個C-N鍵保持完整[5]。並通過2H-NMR證實了這一過程[6]。
酶促研究表明,三個1,5-戊二胺分子通過酶結合的中間體轉化為八氫喹嗪環,且沒有產生任何游離中間體。 最初人們認為1,5-戊二胺是先被二胺氧化酶氧化成5-氨基戊醛[7]。然後5-氨基戊醛自發形成對應的Δ1-哌啶席夫鹼。兩個Δ1-哌啶分子發生以類似羥醛縮合的形式進行偶聯產生亞胺中間體。亞胺進一步水解生成對應的醛和胺。最後伯胺被氧化成醛,並進一步形成亞胺以產生八氫喹嗪環[7]。
17-氧代司巴丁合成酶合成途徑
[編輯]許多酶促實驗表明司巴丁的合成涉及一種叫做17-氧代司巴丁合成酶(17-oxosparteine synthase,OS)的轉氨酶[8][9][10][11][12][13]。這種酶不會產生1,5-戊二胺的脫氨過程(如前面提到的一個氨基脫去生成5-氨基戊醛),因此可以假設八氫喹嗪環的合成涉及了氨基的轉移[11][12][13]。17-氧代司巴丁的合成需要四個丙酮酸單元作為氨基受體產生四個丙氨酸分子。無論是前面的脫氨機理還是本節的轉氨機理,對應的賴氨酸脫羧酶和17-氧代司巴丁合成酶都發生在葉綠體中。[14]
參考文獻
[編輯]- ^ 余健民,洪浪,盛國太 (編). 司巴丁Sparteine. 新编心血管实用药物学. 南昌: 江西科學技術出版社. 2017: 96–97.
- ^ 申泮文,王積濤 (編). 鹰爪豆碱sparteine. 化合物词典. 上海: 上海辭書出版社. 2002: 585.
- ^ Dewick PM. Medicinal Natural Products: A Biosynthetic Approach 3rd. Wiley. 2009: 328–329. ISBN 978-0-470-74276-1. doi:10.1002/9780470742761.
- ^ Golebiewski WM, Spenser ID. Biosynthesis of the lupine alkaloids. II. Sparteine and lupanine. Canadian Journal of Chemistry. 1988, 66 (7): 1734–1748. doi:10.1139/v88-280
 .
.
- ^ Rana J, Robins DJ. Quinolizidine alkaloid biosynthesis: Incorporation of [1-amino-15N,1-13C]cadaverine into sparteine. Journal of the Chemical Society, Chemical Communications. 1983, 1983 (22): 1335–1336. doi:10.1039/C39830001335.
- ^ Fraser AM, Robins DJ. Incorporation of chiral [1-2H]cadaverines into the quinolizidine alkaloids sparteine, lupanine, and angustifoline. Journal of the Chemical Society, Chemical Communications. 1984, 1984 (22): 1477–1479. doi:10.1039/C39840001477.
- ^ 7.0 7.1 Aniszewski T. Alkaloids – Secrets of Life: Alkaloid Chemistry, Biological Significance, Applications and Ecological Role. Elsevier. 2007: 98–101 [2024-07-10]. ISBN 978-0-444-52736-3. doi:10.1016/B978-0-444-52736-3.X5000-4. (原始內容存檔於2024-03-10).
- ^ Wink M, Hartmann T. Enzymology of quinolizidine alkaloid biosynthesis
 . Zalewski RI, Skolik JJ (編). Natural Products Chemistry 1984: A Collection of Invited Section and Colloquium Lectures Presented at the 14th IUPAC International Symposium on the Chemistry of Natural Products, Poznań, Poland, 9–14 July 1984
. Zalewski RI, Skolik JJ (編). Natural Products Chemistry 1984: A Collection of Invited Section and Colloquium Lectures Presented at the 14th IUPAC International Symposium on the Chemistry of Natural Products, Poznań, Poland, 9–14 July 1984 . Studies in Organic Chemistry 20. Elsevier. 1985: 511–520. ISBN 978-0-444-42457-0.
. Studies in Organic Chemistry 20. Elsevier. 1985: 511–520. ISBN 978-0-444-42457-0.
- ^ Wink M. Quinolizidine alkaloids: Biochemistry, metabolism, and function in plants and cell suspension cultures. Planta Medica. 1987, 53 (6): 509–514. PMID 17269092. doi:10.1055/s-2006-962797
 .
.
- ^ Wink M, Hartmann T. Cadaverine–pyruvate transamination: The principal step of enzymatic quinolizidine alkaloid biosynthesis in Lupinus polyphyllus cell suspension cultures. FEBS Letters. 1979, 101 (2): 343–346. PMID 446758. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(79)81040-6
 .
.
- ^ 11.0 11.1 Perrey R, Wink M. On the role of Δ1-piperideine and tripiperideine in the biosynthesis of quinolizidine alkaloids. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung. 1988, 43c (5–6): 363–369. doi:10.1515/znc-1988-5-607
 .
.
- ^ 12.0 12.1 Saito K, Murakoshi I. Chemistry, biochemistry and chemotaxonomy of lupine alkaloids in the Leguminosae. Atta-ur-Rahman (編). Structure and Chemistry (Part C). Studies in Natural Products Chemistry 15. Elsevier. 1995: 537. ISBN 978-0-444-82083-9. doi:10.1016/S1572-5995(06)80142-0.
- ^ 13.0 13.1 Roberts MF. Enzymology of alkaloid biosynthesis
 . Roberts MF, Wink M (編). Alkaloids: Biochemistry, Ecology, and Medicinal Applications
. Roberts MF, Wink M (編). Alkaloids: Biochemistry, Ecology, and Medicinal Applications . Plenum Press. 1998: 112–114. ISBN 978-1-4757-2905-4. doi:10.1007/978-1-4757-2905-4_5.
. Plenum Press. 1998: 112–114. ISBN 978-1-4757-2905-4. doi:10.1007/978-1-4757-2905-4_5.
- ^ Wink M, Hartmann T. Enzymatic synthesis of quinolizidine alkaloids in lupin chloroplasts. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung. 1980, 35c (1–2): 93–97. doi:10.1515/znc-1980-1-218
 .
.


